In this article, we’ll discuss about Components Of Communication Process, how they play a major role in making communication possible.
Components Of Communication Process
The main components of communication process are as follows:
1. Context – Communication is affected by the context in which it takes place. This context may be physical, social, chronological or cultural. Every communication proceeds with context. The sender chooses the message to communicate within a context.
2. Sender / Encoder – Sender / Encoder is a person who sends the message. A sender makes use of symbols (words or graphic or visual aids) to convey the message and produce the required response. For instance – a training manager conducting training for new batch of employees. Sender may be an individual or a group or an organization.
The views, background, approach, skills, competencies, and knowledge of the sender have a great impact on the message. The verbal and non-verbal symbols chosen are essential in ascertaining interpretation of the message by the recipient in the same terms as intended by the sender.
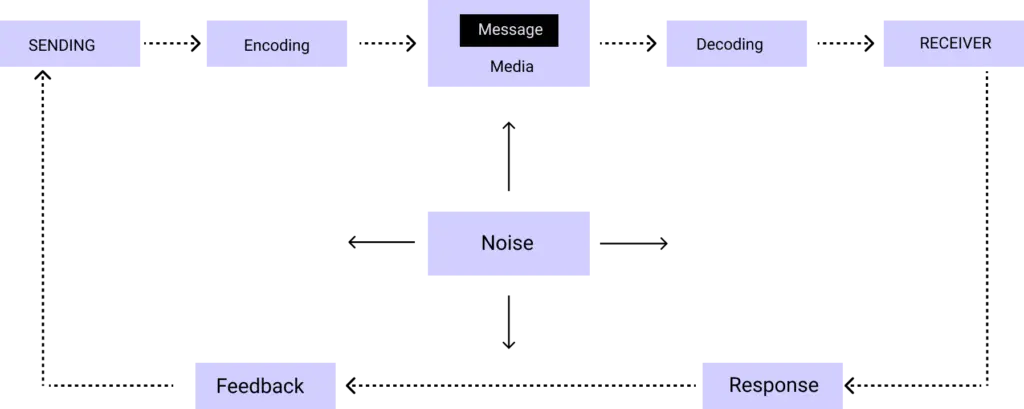
3. Message – Message is a key idea that the sender wants to communicate. It is a sign that elicits the response of recipient. Communication process begins with deciding about the message to be conveyed. It must be ensured that the main objective of the message is clear.
4. Medium – Medium is a means used to exchange / transmit the message. The sender must choose an appropriate medium for transmitting the message else the message might not be conveyed to the desired recipients. The choice of appropriate medium of communication is essential for making the message effective and correctly interpreted by the recipient. This choice of communication medium varies depending upon the features of communication.
For instance – Written medium is chosen when a message has to be conveyed to a small group of people, while an oral medium is chosen when spontaneous feedback is required from the recipient as misunderstandings are cleared then and there.
5. Recipient / Decoder – Recipient / Decoder is a person for whom the message is intended / aimed / targeted. The degree to which the decoder understands the message is dependent upon various factors such as knowledge of recipient, their responsiveness to the message, and the reliance of encoder on decoder.
6. Feedback – Feedback is the main component of communication process as it permits the sender to analyse the efficacy of the message. It helps the sender in confirming the correct interpretation of message by the decoder.
There are two kinds of feedback:
- Positive Feedback: Confirms the source that the intended effect of the message was achieved. Positive feedback tells the source that everything is going in the desired way.
- Negative Feedback: informs the source that the intended effect of the message was not achieved.
Communication Noise
Communication channels are subject to noise. Noise can be identified as the loss of meaning during the transmission.
There are two major types of noise:
1. Channel Noise: This type of noise includes any disturbance, which interferes with the physical transmission of the message. In mass communication channel noise includes static on the radio, ink in the newspaper, a rolling screen in television, or type too small to read in a magazine. In interpersonal communication, someone speaking in a room over another conversation, a door shutting etc.
2. Semantic Noise: This type of noise results in the wrong interpretation of messages, even though the message is received exactly as it was sent such as words too difficult, subject too difficult for receiver to understand also differences of selected meaning of words between the message sender and a receiver, for example receiver thinking that the words prints to something different than that is intended by the sender.
